Description
Revolutionizing Wastewater Treatment with MABR Technology
The Membrane Aerated Biofilm Reactor (MABR) is one of the most recent wastewater treatment technologies that have been developed. It merges advanced gas separation membrane technology with a fixed biofilm process. The innovative system offers an answer to the increasing need for water treatment methods that are both efficient, sustainable and compact. MABR technology improves biological treatment efficiency and reduces energy consumption. It introduces oxygen directly through the membrane in a bubble-free way.
The MABR system is realized through a layered biofilm structure of aerobic and anoxic bacteria that perform simultaneous nitrification and denitrification. High performance for municipal, industrial and decentralized wastewater treatment is facilitated by its unique design. It leads to a cleaner, more sustainable future.

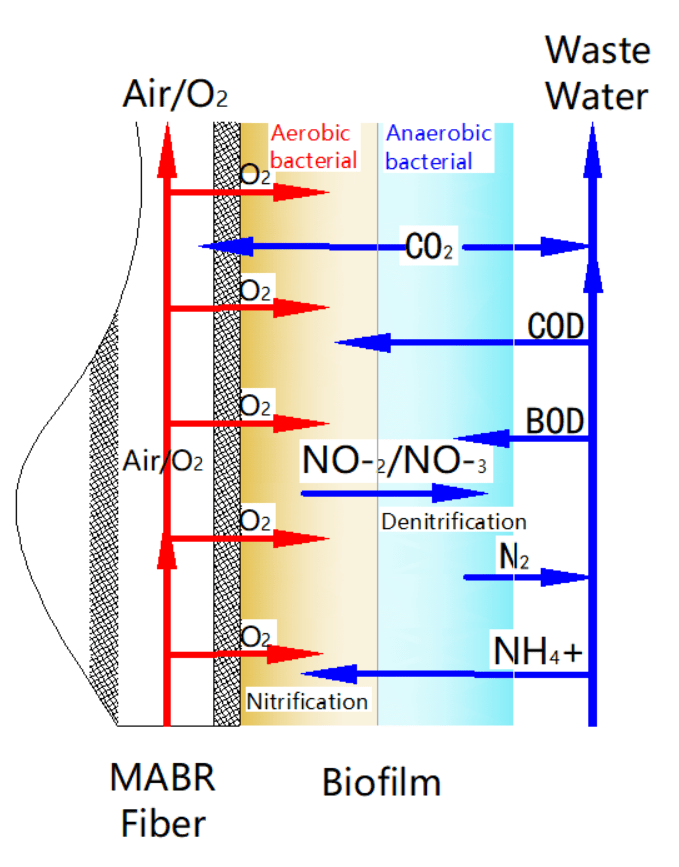


How Does MABR Technology Work?
MABR technology works by incorporating a permeable gas membrane which supplies oxygen to the biofilm. Here’s how the process unfolds:
- Oxygen Transfer: Oxygen molecules remain dissolved in the solution without forming bubbles and the oxygen molecules hence directly transport through the membrane directly to microorganisms at the biofilm.
- Biofilm Formation: Although the layers of biofilm form on the membrane surface, they may not develop naturally on the membrane surface. The inner layer reflects aerobic nitrifying bacteria, outer layer has anoxic denitrifying bacteria.
- Simultaneous Reactions: The system allows both nitrification and denitrification to occur in parallel. Some bacteria like nitrifying behaviour transform ammonia to nitrate and denitrifying bacteria behaviour convert nitrate to nitrogen gas to run efficiently and remove nitrogen.
- Effluent Quality: This flowing water gets out of the system with low concentration of contaminants and hence appropriate for discharge or re-uses.
The bubble-free oxygen delivery and unique biofilm structure set MABR apart from traditional wastewater treatment methods, offering a more energy-efficient and effective solution.
Key Features of MABR Systems
MABR technology stands out for its innovative design and performance-enhancing features:
- Bubble-Free Oxygen Transfer: Maximizes oxygen utilization by delivering it directly to the biofilm.
- Energy Efficiency: Reduces energy consumption by minimizing the need for aeration systems.
- Compact Design: Takes less space as compared to the other treatment systems hence suitable for application in urban and decentralized sectors.
- Simultaneous Nitrification and Denitrification: Results in high nitrogen elimination in a one-stage system.
- Scalability: Can respond as a whole to fluctuations in the quantities of wastewater and their degree of treatment.
Such features make the MABR system preferred by many municipalities and industries as a sustainable wastewater treatment technology.
| Diffuser | Standard Aeration Efficiency |
| Coarse Bubble | 0.5~1.0 |
| Fine Bubble | 3.0~4.0 |
| Surface Aerator | 1.0 |
| Jet Aerator | 1.0 |
| MABR | 12.0~14.0 |
Advantages of MABR Technology
MABR technology offers several benefits that set it apart from traditional wastewater treatment systems:
- High Treatment Efficiency: Aerobic and anoxic biofilms provide the best results in organic matter and nitrogen compounds removal.
- Reduced Energy Costs: Bubble-free oxygen transfer slightly reduces energy expenditure and is more economical.
- Low Maintenance Requirements: This design reduces operational intricacy and maintenance as it is simple, compact and does not require complex engineering proficiency.
- Space-Saving Design: The compact reactor design makes it suitable for even crowded places such as cities and even in locations that are scarcely populated.
- Improved Effluent Quality: MABR systems enable the generation of high-quality treated water with discharge or reuse sewer standards.
- Environmental Sustainability: Reduced energy use and improved treatment efficiency align with environmental conservation goals.
These advantages make MABR an increasingly popular choice for wastewater treatment worldwide.
Applications of MABR Systems
Due to its flexibility of use, MABR technology can be used in various wastewater treatment processes. This includes:
-
Municipal Wastewater Treatment
MABR systems are appropriate for handling domestic sewage in urban and suburban regions. Due to their compact size and high performance. They are ideal for further development or enhancement of current treatment plants.
-
Wastewater Treatment for Industries
MABR is particularly suitable in industries generating high-strength wastewater. Because it offers high efficiency and can treat wastewater of varying concentrations.
-
Decentralized Wastewater Treatment
Remote communities, resorts, and construction sites cannot access centralized water treatment systems. MABR systems are virtually a low-cost, low-maintenance decentralized wastewater treatment system.
-
Reuse and Water Recycling
With increasing water scarcity, MABR systems are instrumental in producing treated water suitable for reuse in irrigation, industrial processes, and other non-potable applications.
The flexibility of MABR technology ensures it meets diverse wastewater treatment needs across sectors.
How MABR Compares to Conventional Systems
MABR technology brings significant improvements over traditional wastewater treatment systems. Here are key comparisons:
| Feature | MABR | Conventional Systems |
| Oxygen Transfer Efficiency | High (Bubble-Free) | Moderate (Bubble-Based) |
| Energy Consumption | Low | High |
| Footprint | Compact | Large |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate to High |
| Treatment Performance | High (Simultaneous Reactions) | Moderate |
Environmental Impact of MABR Technology
MABR systems contribute to environmental sustainability through:
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Lower energy requirements decrease greenhouse gas emissions.
- Efficient Resource Use: Bubble-free oxygen delivery optimizes the use of resources.
- Improved Water Quality: Treated effluent protects ecosystems and supports water reuse initiatives.
- Space Efficiency: Compact designs minimize land use, preserving natural habitats.
These environmental benefits make MABR a valuable tool in addressing global water and sustainability challenges.
BUBBLE DIFFUSER
High energy consumption
Large bubbles float up and release
Short contact time
Low oxygen utilization rate
MABR MOLECULAR DO
Low energy consumption
Molecular Oxygen Transfer
Oxygen directly supply to biofilm
High oxygen utilization rate
| NO. | Items | Unit | OX-MABR |
| 1 | Materials | – | Polymer |
| 2 | Pore size | μm | Dense and non-porous |
| 3 | Fiber Breaking Intensity | N | ≥150 |
| 4 | Burst Pressure | Kpa | ≥500 |
| 5 | Air permeability | L/㎡.h.bar | >0.1 |
| 6 | (OTR) Oxygen Transfer Rate | g O2/㎡.d | 6~20 |
| 7 | COD removal | g COD /㎡.d | 5~25 |
| 8 | Ammonia removal | g N/㎡.d | 1~3 |
| 9 | Processing Pressure | Kpa | 5~100 |
| 10 | Processing Airflow | L/㎡.h | 0.05~0.1 |
| 11 | Processing Temp | ℃ | -40~120℃ |
| 12 | Membrane Feature | – | Poreless structure bubbleless molecular
oxygen transfer;low energy saving SND;Biocompatibility;No Membrane clogging |
| 13 | Application | – | Anammox,Anoxic, Aerobic |
SPECIFICATION of MABR Systems
| Model | Membrane Area | Length | Width | Thickness | Port |
| MABR-10 | 10m2 | 2000 | 535 | 45 | 32 |
| MABR-15 | 15m2 | 2000 | 535 | 45 | 32 |
| MABR-20 | 20m2 | 2000 | 630 | 50 | 25 |
| MABR-25 | 25m2 | 2000 | 630 | 50 | 25 |
| MABR-30 | 30m2 | 2300 | 630 | 50 | 25 |

MABR CASSETTE
| Model | Membrane Area | Length | Width | Height |
| MABR-480 | 480m2 | 2020 | 1450 | 2250 |
| MABR-1000 | 1000m2 | 2100 | 1450 | 2250 |
| MABR-1920 | 1920m2 | 2300 | 1450 | 2550 |

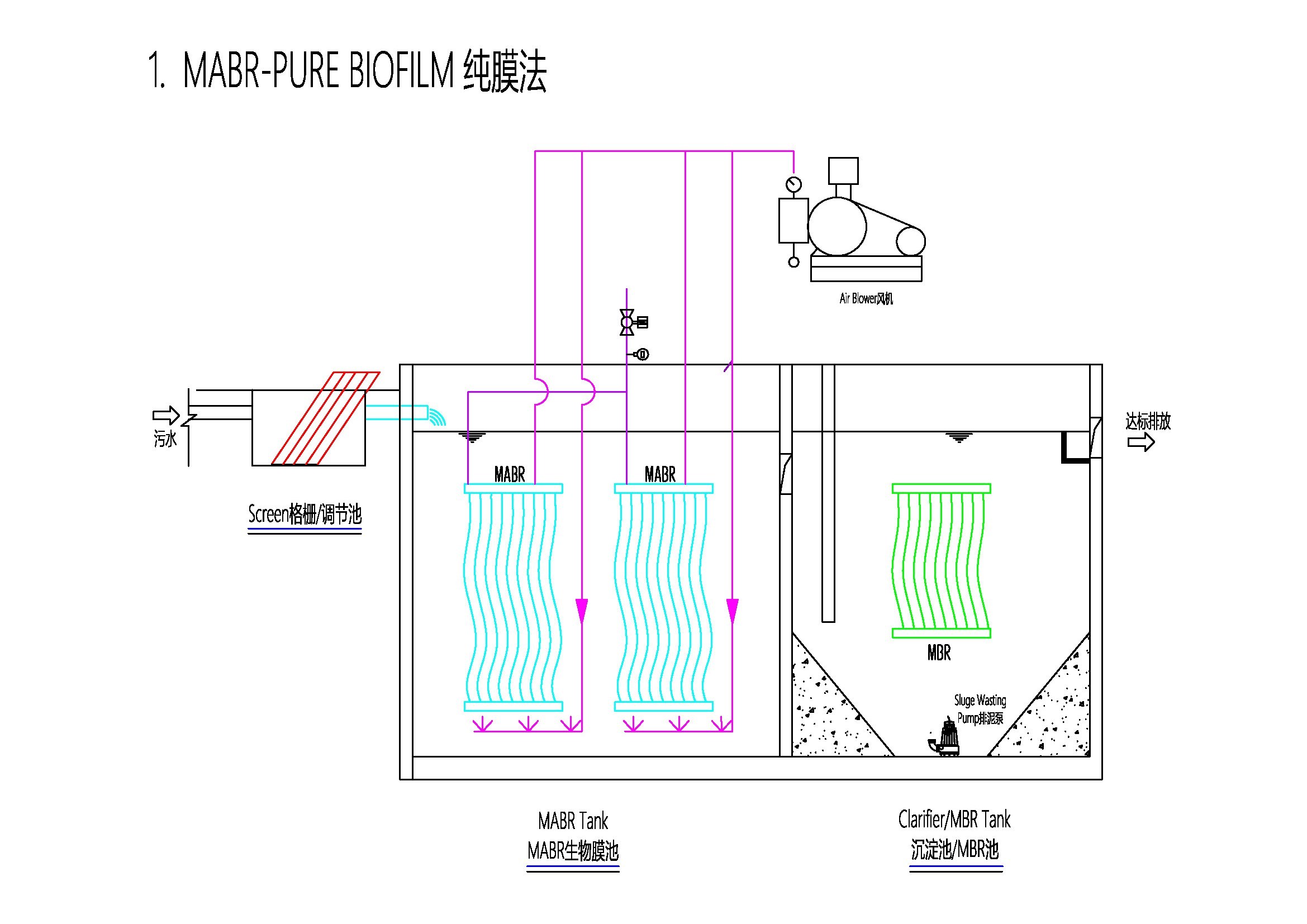
MABR PURE Biofilm
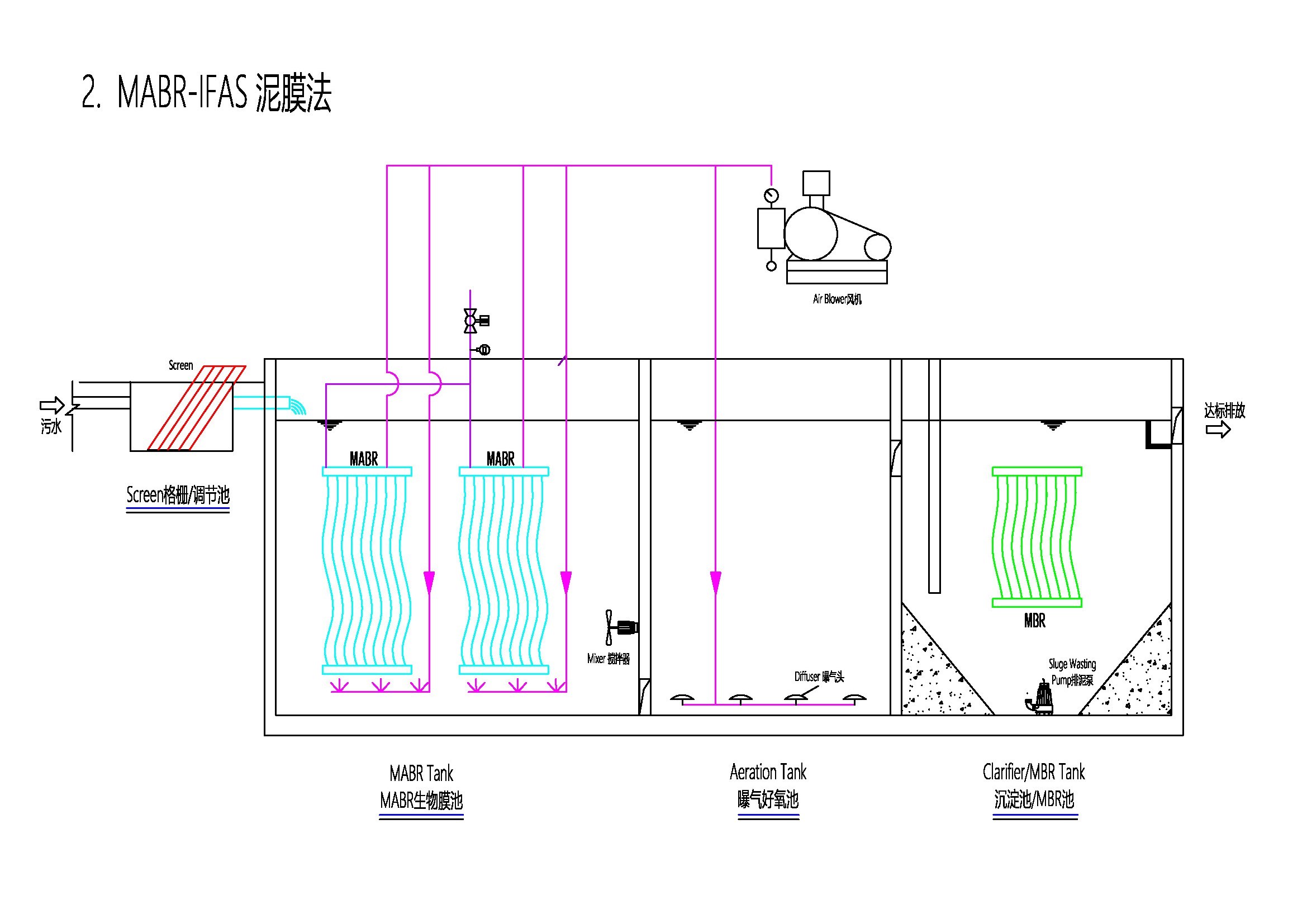
MABR IFAS
Challenges and Considerations
While MABR technology offers numerous advantages, there are some challenges to consider:
- Initial Costs: MABR systems may have higher upfront costs compared to conventional systems.
- Operational Expertise: Proper training and knowledge are required to optimize system performance.
- Scaling for Large Volumes: Adapting MABR systems to handle very large wastewater volumes may require innovative designs.
Overcoming these challenges through subsequent studies will also improve the implementation of MABR.
Conclusion
The Membrane Aerated Biofilm Reactor (MABR) is supposedly the first of the new generation wastewater treatment technologies. A system that is efficient and highly versatile. Through the use of highly developed membrane technology integrated with fixed biofilm technology. MABR systems provide efficient and high-standard treatment without putting much pressure on energy consumption and the environment. From municipal sewage through industrial effluent and decentralized systems. MABR is introducing a new paradigm in how wastewater is treated.
This makes MABR systems the best option for modern wastewater treatment needs. Because investing in such a system is investing in a cleaner, more sustainable future for all.










Daniel S –
This MABR has transformed our wastewater treatment process—energy-efficient and reliable.
Megan H –
Highly effective, especially in low-energy applications. Bit of a learning curve initially.